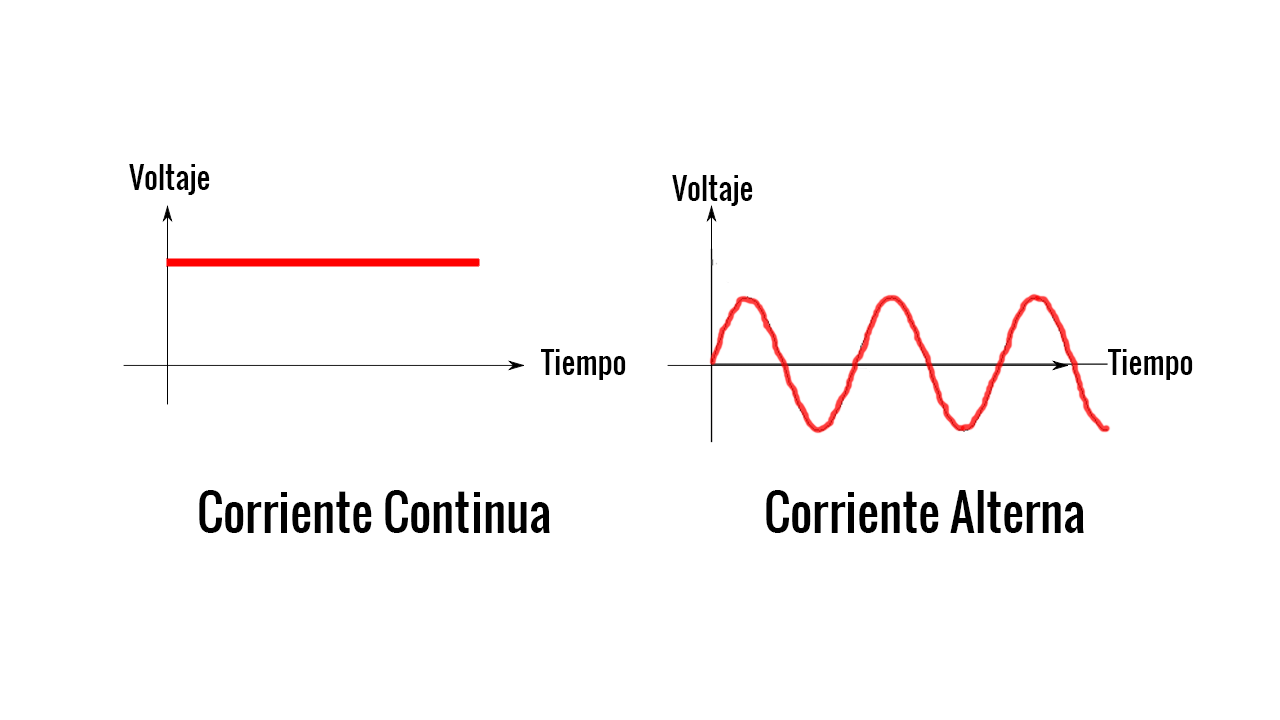
1) ALTERNATE CURRENT: This type of current is produced by the alternators and is what is generated in the power plants . The current that we use in the plugs or sockets of the houses is of this type. This type of current is the most common because it is the easiest to generate and transport. The alternator spins its turns (rotor) 50 times every second generating a wave of sinusoidal and sinusoidal current and voltage . This speed of rotation is said to have a frequency of 50Hz (turns per second). In America it is 60Hz.
DC: the direct current they produce it batteries , batteries and dynamos . between the ends of any of these generators a constant voltage is generated that does not vary with time. For example, if the battery is 12 volts, all s receivers that connect to the battery will always be at 12 volts (unless the battery is worn out and has less stress). If you do not have clear the magnitudes of voltage and intensity, and what is the electrical current, we recommend that you first see the links at the bottom.
2) INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES: These devices allow the user of the computer to enter data, commands and programs in the CPU. The most common input device is a keyboard similar to that of typewriters.
Keyboard: The keyboard is an effective device for entering non-graphic data such as associated picture labels with a display of graphics. The keyboards they can also be offered with features that facilitate the entry of screen coordinates, menu selections or graphic functions.

Mouse or Mouse: It is an electronic device that allows us to give instructions to our computer through a cursor that appears on the screen and clicking to carry out a certain action; As the Mouse rolls on the desktop, the cursor (Pointer) on the screen does the same.

Microphone: The microphones are the transducers responsible for transforming acoustic energy into electrical energy, allowing, therefore, the recording, storage, transmission and electronic processing of audio signals.

Scanner: It’s a unity of data entry. It allows the introduction of graphic images to the computer.

Digital camera: It connects to the computer and transmits the images it captures, which can be modified and retouched, or take it again in case it is wrong.

Video camera: Record videos as if from a normal camera, but the advantages offered by being in digital format, which is much better image .

Webcam: It is a camera of small dimensions. It’s just the camera, it does not have an LCD. It has to be connected to the PC in order to work, and it transmits the images to the computer.

Output Devices: These devices allow the user to see the results of calculations or data manipulations of the computer.
Screen or Monitor: It is where you see the information provided by the computer.

Printer: it is the peripheral that the computer uses to present information printed on paper.

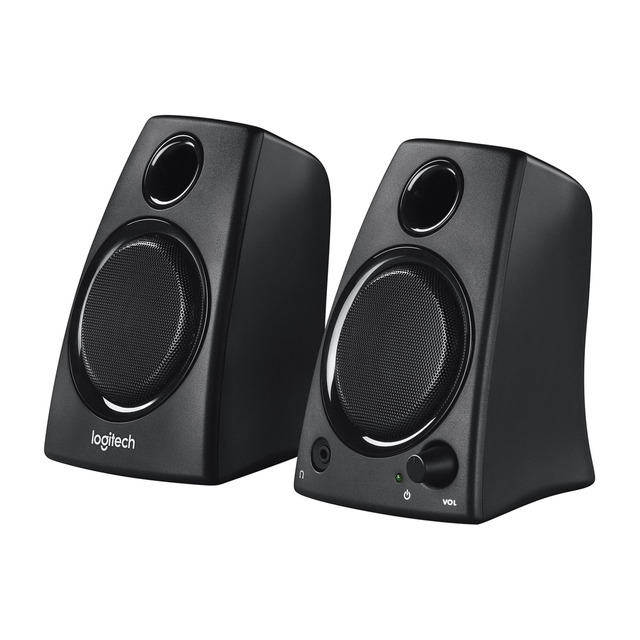
Speakers: Devices by which sounds are emitted from the sound card.

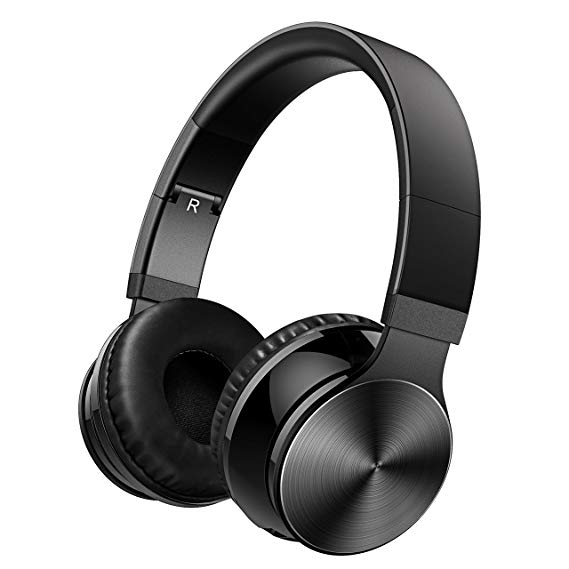
Headphones: They are devices placed in the ear to be able to hear the sounds that the card of sound sends. They have the advantage that they can not be heard by another person, only the one who uses them.

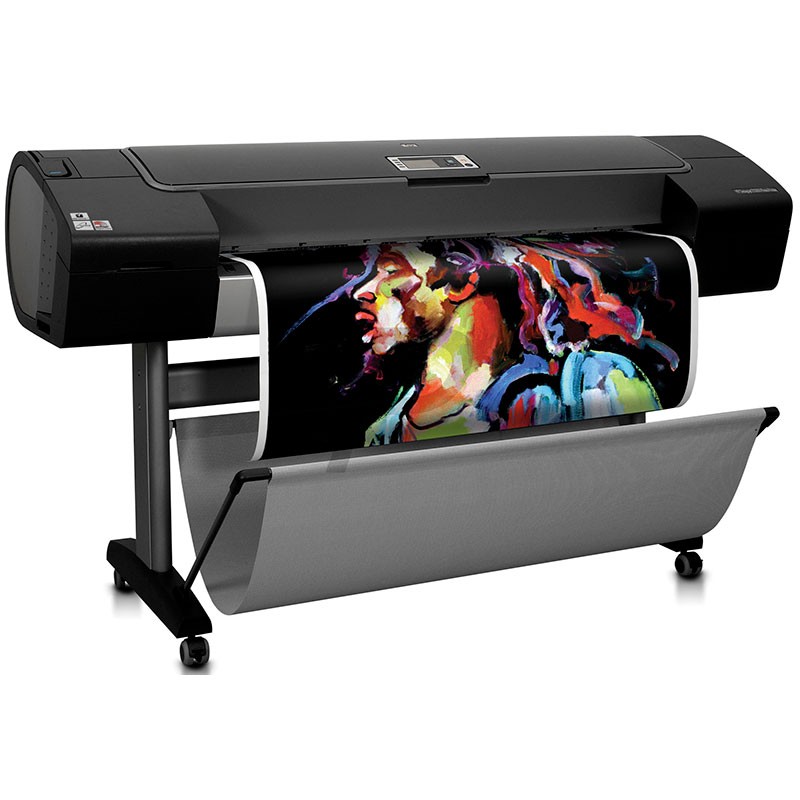
Plotters: There are plotters for different maximum sheet sizes (A0, A1, A2, A3 and A4); for different qualities of output sheets (bond, carbon, acetate); for different line thicknesses of drawing (different thicknesses of rapidógrafos), and for different colors of drawing (different colors of ink in the rapidógrafos).

Fax: Device by means of which a copy of another printed form is printed, transmitted either by telephone or from the fax itself. A roll of paper is used for this, which is cut off when the printing is finished.

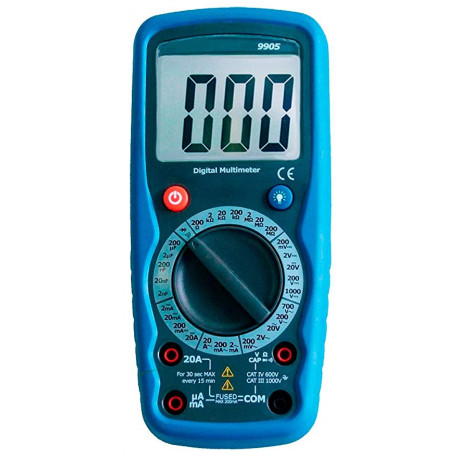
3) MULTIMETER: A multimeter, sometimes also called multimeter or tester, is a measuring instrument that offers the possibility of measuring different electrical parameters and magnitudes in the same device. The most common are those of voltmeter, ammeter Y Ohmmeter It is frequently used by staff throughout the range of electronics Y electricity

4) POWER CABLE : A power cable refers to the cable that connects the computer to the system electric and that gives the power (electricity) to it It is the cable that goes from the power socket (or from the plug of the stabilizer tension electrical) to the power source (or source of Energy electrical) of the computer, usually located in the upper rear part of the cabinet.

5) SOURCES OF POWER (AT, ATX, MINIATX). REAL WATTS?
AT : motherboard. The two remaining types, of which there is a variable amount, feed the peripherals not plugged into a slot of the motherboard, such as hard disk drives, CD-ROM drives, floppy drives, etc.

ATX: it ‘s very similar to the AT, but it has a series of differences, both in its operation and in the voltages delivered to the motherboard. The ATX Source actually consists of two parts: a main source, which corresponds to the old AT source (with some aggregates), and a assistant
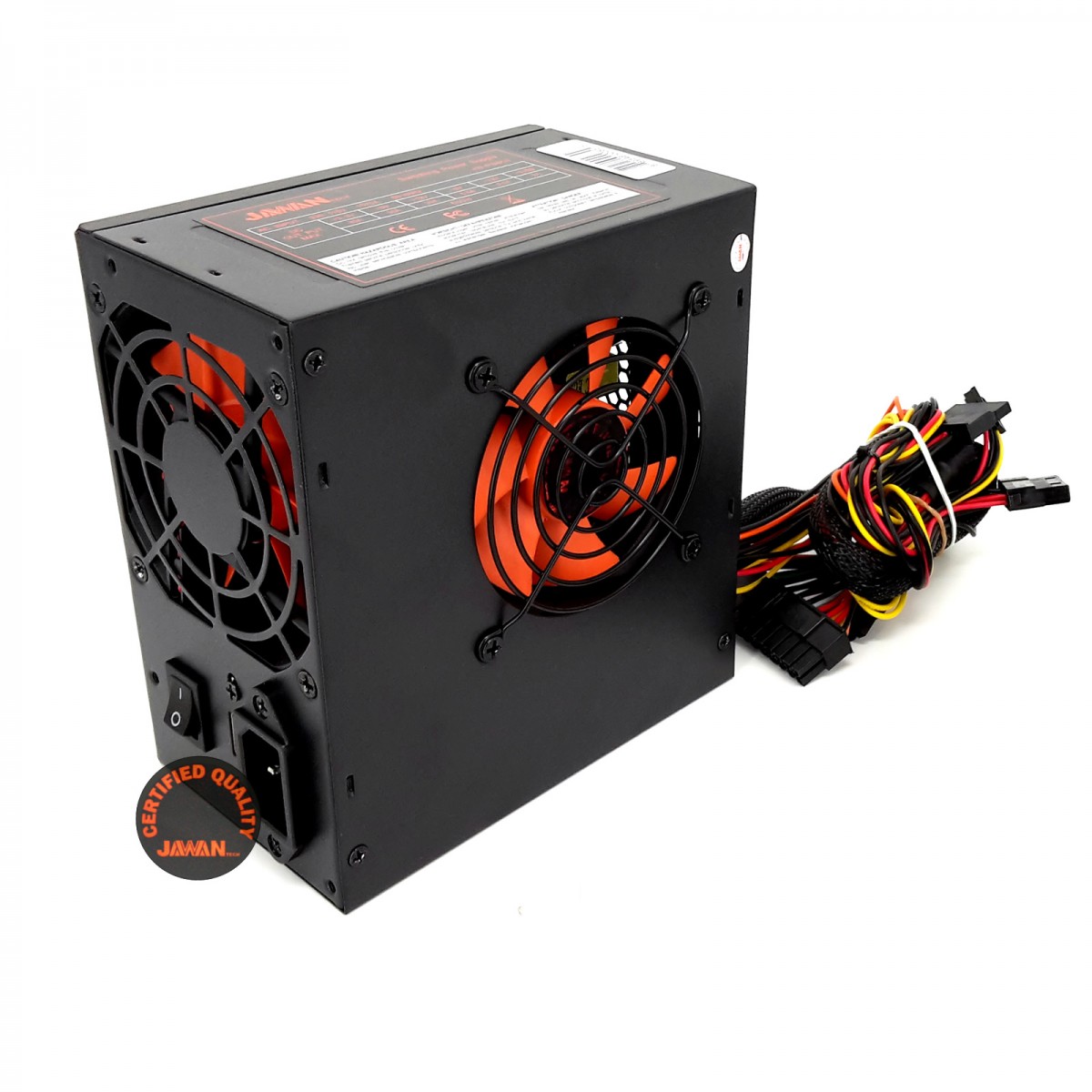

MiniATX : It’s a power source for a motherboard format fully developed by VIA Technologies. Although it is a proprietary source format, its specifications are open. In fact, other manufacturers have products in this format.

REAL WATTS
6) SOURCE CONNECTORS (ATX 20/24 PIN, ATX P4, MOLEX, SATA, PCI EXPRESS)
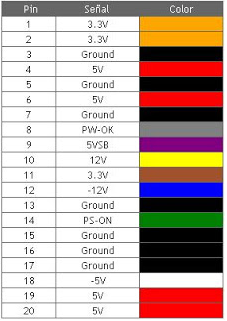
ATX Connector 20/24 Pin: It is the one that feeds the motherboard, formerly 20 pins, the current standard provides 24 pins. It is almost always composed of a block of 20 pins, to which we can add a block of 4 pins. This in order to respect the compatibility with the old plates with 20 pin connectors.

ATX P4: (or also ATX 12V), connects to the motherboard and is exclusively for the processor power, without it it is impossible to start the computer
Currently most motherboards have 8 pins, due to the increase in CPU power.

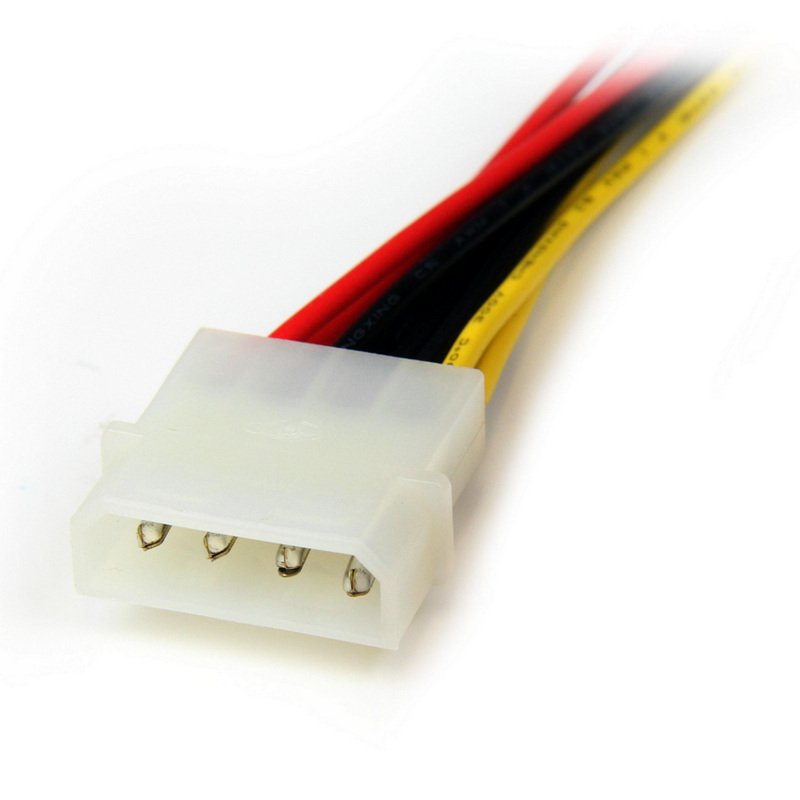
Molex: The most classic and still present in all computers, sometimes used directly on the motherboard, serves to connect the hard drive and all types of drives (reader, recorder).

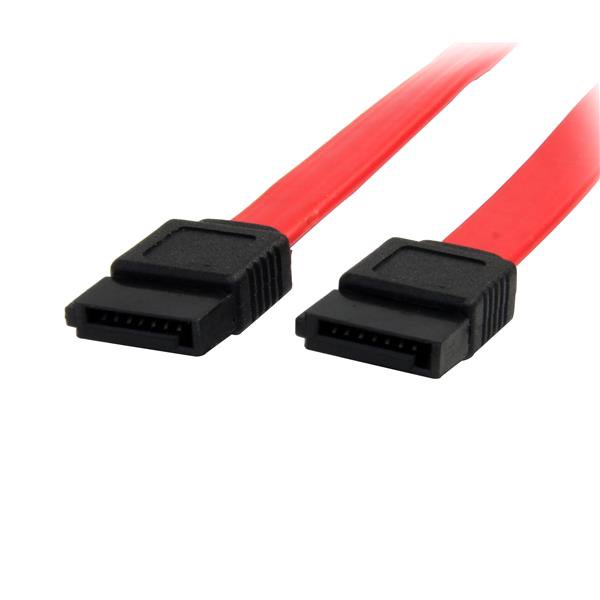
Sata:
It is present in all modern computers, it is used to power hard drives and recorders under the SATA standard.

PCI Express connector:
The power of the cards graphs it does not stop to increase, many of them need a source of direct feeding of the main block (sometimes even two). This is the function of this connector. Initially of 6 pins, more and more we can find them of 8.
7) MAINBOARD (MOTHER CARD ): The Motherboard, motherboard or motherboard is a card of printed circuit that allows the integration of all the components of a computer. For this, it has a basic software known as BIOS, which allows you to fulfill your functions. The mother card houses the connectors needed for the processor, RAM, ports and the rest of the boards (like the graphics card wave network card

The board, motherboard, or motherboard is the main element of any computer, in which all other devices and devices are located or to which they are connected.
8) USB PORTS 1.0 – 2.0 – 3.0, TYPE-A, TYPE-B, TYPE-C, USB MINI, USB MICRO, PS / 2, ETHERNET (RJ45, SPEED (10,100,1000)). SERIAL, PARALLEL, EXTERNAL SATA.
USB 1.0 : The first, designed to work with keyboards, mice and devices that require a very small bandwidth. It allows to work at an approximate speed of 1.5 Megabits per second. With this you would need approximately 6 hours to copy a 4 Gigabyte movie. It appears in the year 1996.

USB 2.0: With this we have a huge jump. Multiply the speed by 40 times to reach 480 Megabits per second. The same movie as in the previous example would take a little more than 1 minute to copy. We are already in the year 2000. It is very common to find PCs that incorporate both ports, USB 1.x and 2.0 then it is very important to know what you are connecting your devices especially if you are going to make copies of very large files.
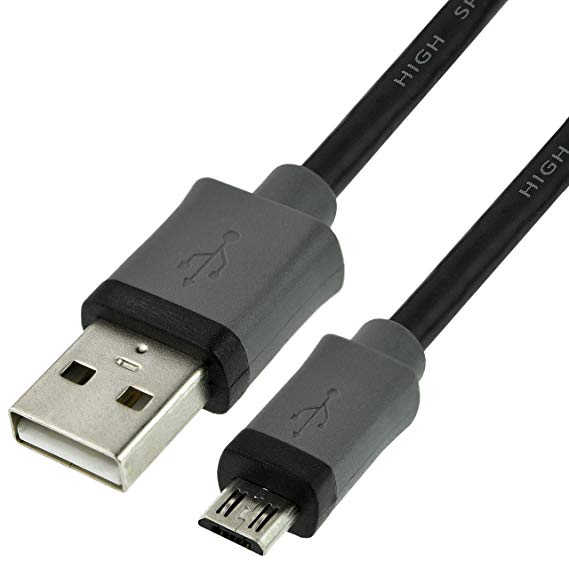

USB 3.0: Appears in 2008. Multiplies the speed up to 4.8 Gigabits, that is, it is 10 times faster than USB 2.0. The same movie would take only 10 or 15 seconds to copy. Now the problem, for the first time, is not the cable but the HDD or device you connect fast enough to give you that speed

.
Mini USB: The mini USB connectors are smaller than their standard USB counterparts and have a fifth pin. The fifth pin is known as the ID pin and is typically not used in mini USB connectors. It was designed to later allow the improvement of USB technology. The mini USB connectors have a life cycle of at least 5,000 connections and disconnections, which accommodates the mobile nature of the devices that are designed to interact. Standard USB connectors are usually used with devices that are stationary and do not disconnect often.

Micro USB: Since electronic devices such as cell phones continue to get smaller, most new devices are incorporating micro USB connectors. Created in 2007, the micro USB connectors are smaller than their mini USB counterparts and have a life cycle of at least 10,000 connections and disconnections.

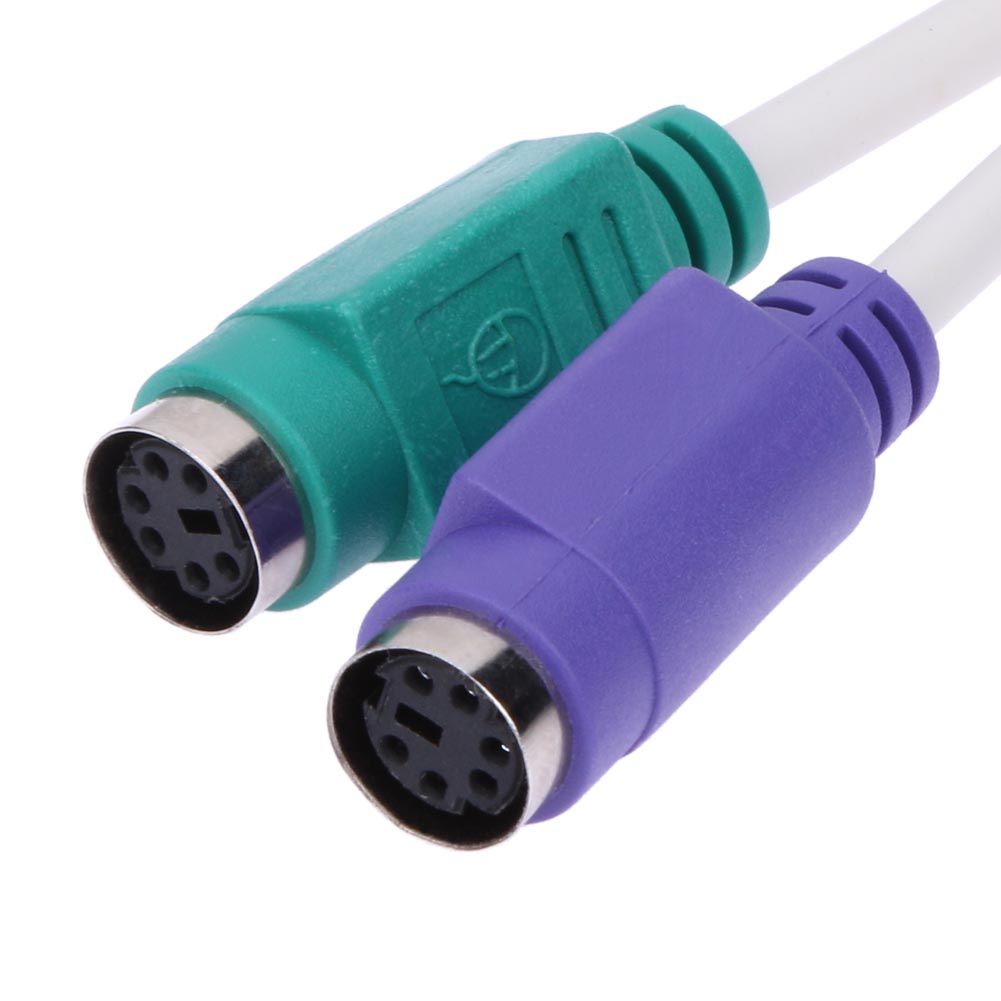
PS / 2: The connector PS / 2 o PS / 2 port takes its name from the computer series IBM Personal System / 2 which is created by IBM in 1987 , and used to connect keyboards Y mice . Many of the advances presented were immediately adopted by the PC market, this connector being one of the first. In both cases it is serial (bidirectional in the case of the keyboard), and controlled by microcontrollers located in the motherboard . They have not been designed to be hot-swapped, and the fact that doing so does not usually occur is more because modern microcontrollers are much more resistant to short circuits in their input / output lines

Ethernet: it is a standard of networks of computers of local area with access to the medium by contention CSMA / CD («Multiple Access for Carrier Detection with Collision Detection»), is a technique used in Ethernet networks to improve its performance. The name comes from the concept physical of etherEthernet defines the physical level signaling and wiring characteristics and the data frame formats of the data link level of the model OSI .

RJ45 : The RJ45 connector is a standard network connector, which allows the interconnection of network devices with each other through a UTP cable of 4 pairs (8 cables). There are two ways to connect these connectors to the cables:
* Manually crimp with a pliers.
* Through an industrial vacuum process that fixes the contacts and the connector to the cable.
Normally this connector is manufactured in plastic, and its metallic connections. Transparent plastic is used for the connectors that are attached to the cables manually, in this way, it can be seen if the twisted pairs are connected correctly.

SPEED (10,100,1000
The 10/100/1000 Ethernet extenders allow you to extend Ethernet services beyond the general limits of IEEE 802.3 of 328 feet / 100m using any existing copper cabling previously used in alarm circuits, circuits E1 / T1, RS-232, RS-422, RS-485, CCTV and CATV. In those environments in which an extension of the LAN is made 10/100/1000 Y security of the network is critical, Perle offers the Managed Gigabit Ethernet Extenders that are compatible with all the services of Authentication, authorization and accounting security (AAA) which are used in corporate networks, including TACACS +, RADIUS, LDAP, Kerberos, NIS and RSA .

SERIAL: The serial port, serial port or COM communication port, is a communication interface between computers and peripherals which sends and receives BIT information through BIT, between the serial ports can be mentioned the port of the old models of keyboards and modems . A serial port has a standard connector and works with a protocol that allows the connection of devices to the computer. It is called «serial» because the serial port «serializes» the data. This means that it takes one byte of data and transmits the 8 bits of the byte one by one.

PARALLEL: Parallel port. It is an interface between a computer and a peripheral . The parallel port transmits the information byte per byte, that is to say that the 8 bits of data that form a byte travel together. An example of a parallel port is the port of the printer. The Parallel Port was only created and used for the printers interface and the PC Today we see that it is one of the most used to connect various peripherals to your PC because of its high speed and reliability in the transmission of data, which has been perfected every day.

EXTERNAL SATA : The interface external SATA (eSATA or ESATA) was standardized in mid-2004, with specific definitions of cables, connectors and signal requirements for external units.
It is characterized by:
Speed of SATA on external drives (115 MB / s with external RAID have been measured).
Without conversion of PATA / SATA protocols to USB / Firewire , all disk features are available to the host.
The cable length is restricted to 2 meters; USB and Firewire allow greater distances.
The minimum and maximum transmission voltage was increased to 500mV – 600mV (from 400mV – 600mV)
Voltage received decreased to 240 mV – 600 mV (from 325 mV – 600 mV).
Disposition capacity of the disks in RAID 0 and RAID .

9) VIDEO PORTS (S-VIDEO, HDMI, VGA, DVI, SCART, DISPLAY PORT, MINI DISPLAY PORT)
S-VIDEO : It is a circular connector of the family miniDIN , with the physical structure similar to the connector for keyboards. It allows a better quality of video with improved images, since it increases the b walks because of the information in the luminance . It differs from the composite video used by other standards because the luminance and color are sent independently by different cables. Commonly, it is found on graphics accelerator cards and video capture cards. S-Video has more quality than composite video, since the TV It has separately the information of brightness and color, while in the composite video are together. This separation causes the S-Video cable to have more bandwidth for the luminance and get more effective work from the decoder of chrominance

VGA: is the oldest standard of the three, was introduced in 1987. VGA is an analog signal that handles only video, not sound, does not manage security or digital rights. Video quality is susceptible to the quality of the cable and the distance from the computer to the monitor. If the connector has small thumbscrews on the sides of the cable it is a VGA. Because of this, the VGA image quality can vary considerably depending on the type of cable brand. The VGA connector is usually blue or black, has fifteen pins distributed in three horizontal rows and has a trapezoidal shape.
DVI: was invented in 1999 and is similar to VGA and HDMI. DVI allows you to send video but not audio, you can send digital signal, analog, or both. DVDI allows managing digital rights management and can be converted to HDMI or VGA using a converter. DVI is considered a midpoint between VGA and HDMI, being practically the successor of VGA.
HDMI: first appeared in 2002, is often found on modern TVs, but it is also found on most monitors of the newer computers. If DVI is the successor of VGA, HDMI is a possible successor of DVI, possibly due to its appearance in high definition television. HDMI is a digital standard (1 or 0) that allows to transmit both audio and video. Conditions such as the quality of the cable, the distance from the machine to the monitor or the metal type of the connector does not affect the transmitted signal. HDMI can also handle security, which means that certain types of signals, such as paid television can be blocked before traveling over an HDMI cable.

EUROCONECTOR : The scart is a connector normalized of 21 connections or pins , which exchanges audio and video information. The euroconnector facilitates the connection of televisions , videos , DVD , DTT , satellite receivers , computers (You can use even an adapter VGA -Euroconnector 1 ), Video Consoles , and other devices quickly and with good quality. The connector is designed in such a way that an erroneous connection is not possible, and with all the necessary signals in a single cable. By having separate input and output signals it is possible to chain several devices with two connectors without degrading the signal by conversions. As its voltages are somewhat high (1V) the signal has good immunity to noise.

DISPLAYPORT: (DP) is an interface for connecting digital video managed by VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) and designed as a replacement for the DVI standard in computer equipment. It is similar to the standard HDMI specification, both support audio and video, but unlike HDMI, DisplayPort is a computer interface more than an interface for home theater. DisplayPort allows a high performance, robustness and versatility of the screen, in addition to a high degree of integration with the systems, and a greater interoperability between the different types of devices.

MINI DISPLAY PORT: The Mini DisplayPort port is a reduced version of the digital audio and video interface DisplayPort.
Video signal : WSXGA, 1080p , WQXGA ; Maximum 2K x 1K (2560 x 1600)
Type : Digital Video / Audio / Data Connector
Pines : 20 (external connectors); 32 (internal connectors for laptops)
Audio signal : Optional; DRA, Dolby MAT, DTS HD ; Maximum 8 channels without compression 192 kHz, 24-bit , 6.144 Mbit / s

10) MONITORS CTR, LCD, PLASMA, LED (OLED, AMOLED, SUPER AMOLED), CURBOS, TACTILE, MULTITACTIL.
CTR: CRT monitors use the red, green and blue analog video signals in varying intensities to generate colors in the RGB color space. These have practically exclusively used progressive scanning since the mid-1980s.

LCD: It is a thin and flat screen formed by a number of color or monochrome pixels placed in front of a light source or reflector. It is often used in battery-powered electronic devices because it uses very small amounts of electrical energy.

PLASMA: They are based on the principle that by passing a high voltage through a low pressure gas, light is generated. These screens use phosphor as the CRT but they are emissive like the LCD and in front of these they obtain a great improvement of the color and a great angle of vision. These screens are like fluorescents, and each pixel is like a small colored bulb, the problem with this technology is the length and size of the pixels, so its most common implementation is on large TV screens.

LED: It is a video device that uses LEDs by arranging them in the form of a matrix using diodes of different RGB colors to form the pixel.

OLED: it’s not something new. For several years now it has been used, especially on smaller screens such as cell phones, portable video game consoles and monitors.
But the technology was not quite ready for the big screen … until now. OLED has many advantages over other types of screens.
AMOLED : is an acronym for English, whose meaning is «Active matrix of organic light-emitting diodes». Well, the term should not win, we could say that it is a type of screen that allows you to control the pixels, independently. It is also possible to control its color and its intensity. One of the biggest advantages of this technology is that the pixels are turned off in areas that do not need to show color, without the need to use light and thus spend energy.
Super Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode or Super AMOLED is a screen technology (variant of the AMOLED ) mainly for use on mobile devices and tablets (see the list at the end for examples). One of the main differences of other screen technologies is that the layer that detects the touches is integrated into the screen, instead of being superimposed on the top.
Compared with the first generation of AMOLED, some of the advantages of Super AMOLED are brighter screens, lower reflection of sunlight and lower energy consumption.

MULTI-TOUCHING is a form of computer interaction in which fingers are usually used to directly touch the screen or a touch pad and control a device.

TACTIL : The touch screen is as it says the own expression a screen that shows certain information, which can be modified by clicking directly on the screen itself.
There are two types of touch screen, resistive and capacitive. The first type, resistive, are cheaper but have less brightness and are thicker since they consist of two thin layers of conductive material electric current , between these two layers there is another that does not conduct the current, when pressed on the screen the first layer comes in contact with the second and a circuit interprets where that encounter has occurred. Can be used with gloves and special screen pencils

.
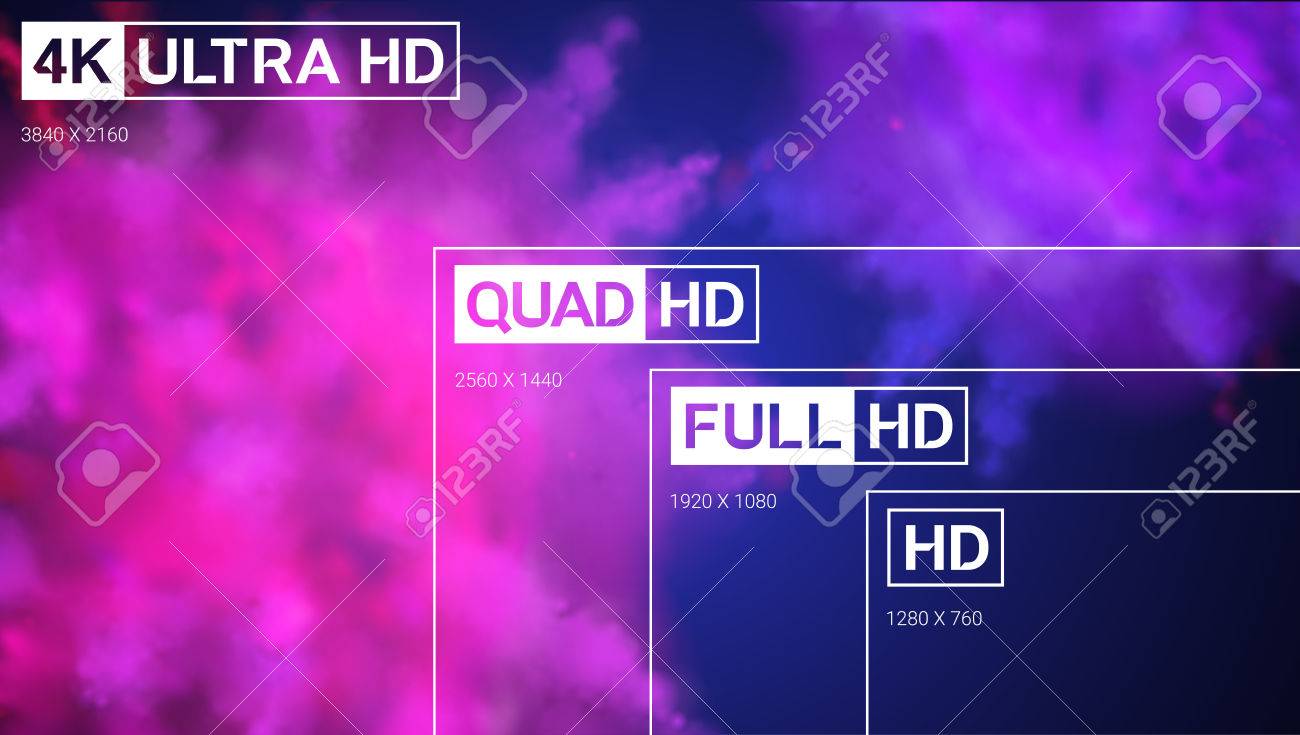
11) DISPLAY RESOLUTIONS (HD, HDR, FULL HD, WUXGA, 2K, 4K, 8K)
HD resolution (1280 X 720)
Before starting to list the resolutions, it should be added that the ones we are going to see they are not all that exist or they have existed but, yes the ones that we can find in current mobile market. Going back to the subject, we go with the lowest resolution we find today: HD resolution.

Full HD resolution
This is the resolution that we most find ourselves lately in the phones that have been arriving to the market despite the invasion of the extra-long panels, and that allows to show 1,920 x 1,080 pixels. This type of resolution initially started with televisions, but it made the leap to smartphones in 2012 with the HTC J Butterfly .
Since then, Full HD resolution has been used in both high-end phones and the Samsung Galaxy S5 or the iPhone 7 Plus as in more restrained phones in specifications as the Moto G4 , the ASUS Zenfone 2 or the Galaxy A7. Despite the extension of this resolution, manufacturers have been seduced for a while by the next level: the QHD resolution .
HDR : High definition (HD) screens are increasingly popular. However, according to an article published this week in Technology Review, a new technology known as HDR (high-dynamic range), is advancing rapidly and some experts believe it could be a rapid successor of high definition. While HD screens use more pixels, HDRs provide more contrast, making the images look much more realistic

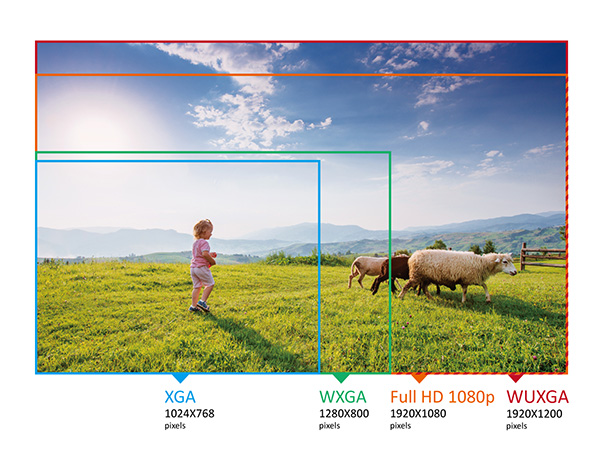
WUXGA : Wide Ultra eXtended Graphics Array or WUXGA is a graphical display mode of computers , including video cards Y monitors .
These systems have evolved over time, going through some as well known as the primitive CGA , VGA , SuperVGA , XGA Y UXGA , increasing in each system the resolution and the number of colors. These so-called systems usually refer to non-panoramic monitors, that is, in 4: 3 format.
When we refer to 16: 9 or 16:10 widescreen format we add to the beginning of the previous abbreviations W, so WUXGA is an adaptation of UXGA mode for panoramic monitors.
WUXGA has a resolution of 1920×1200, equivalent to 2.3 Megapixels .
2K: High definition follows its evolution and increases to 2K, a resolution that has 2048 x 1080 pixels and it corresponds to some 2.2 mega pixels . With this term you have to be careful, because in many places we will find mobile phones with 2K screen but with a higher resolution. What does this mean? Well, in the world of smartphones, the 2K resolution refers to QHD. Therefore, terminals that incorporate 2K screen will actually have 2560 x 1440 pixels (QHD). For example , the Huawei Honor V8 that was released a few months ago.

4k : It is a resolution used in film production and projection, known to have 4096 horizontal pixels and 2160 vertical pixels.
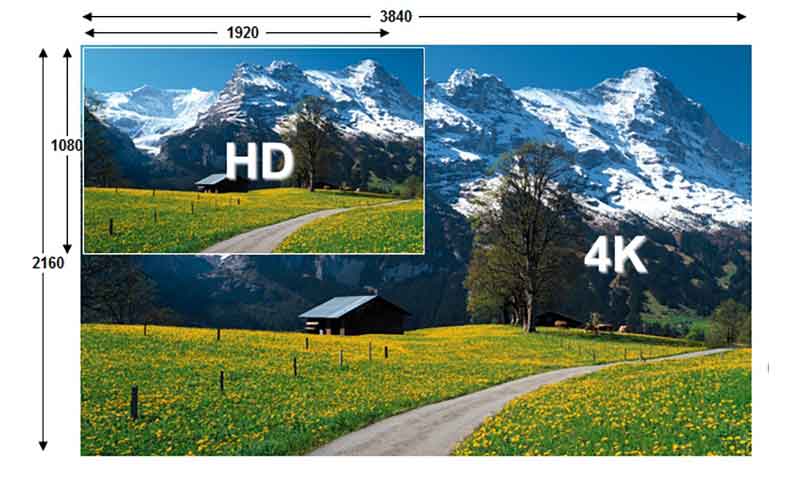

8k : It is the resolution of ultra high definition screen that has 7680 horizontal pixels and 4320 vertical pixels.

12) PUERTO FIRE WIRE (IEEE 1394), SOUND JACK 3.5 MONO AND STEREO, THUNDERBOLT, TOSLINK, RCA, S / PDIF
Fire wire port (IEEE 1394 : The WireFire port is a type of input and output connection to provide high-speed communication between multimedia devices. It works through the serial data transfer, just like a USB port and is mainly used to connect professional digital cameras, printers and other devices in which we typically find the USB port.

The 3.5 mm jack has always been with us to take the sound to our headphones, or to our speakers with auxiliary output … it has been by our side a lot of time, we have given it a lot of use in a large part of our devices, and it is tremendously extended to today becoming almost a standard in sound.

Mono and Stereo: Stereo or stereo sound is a Recording and reproduction method that creates an illusion of direction and audible perspective. This is achieved by using two or more independent audio channels through two or more speakers. In such a way that creates the impression that the sound is heard from several directions, as in natural hearing. Mono or monaural sound is a recording and playback method that uses only one audio channel.

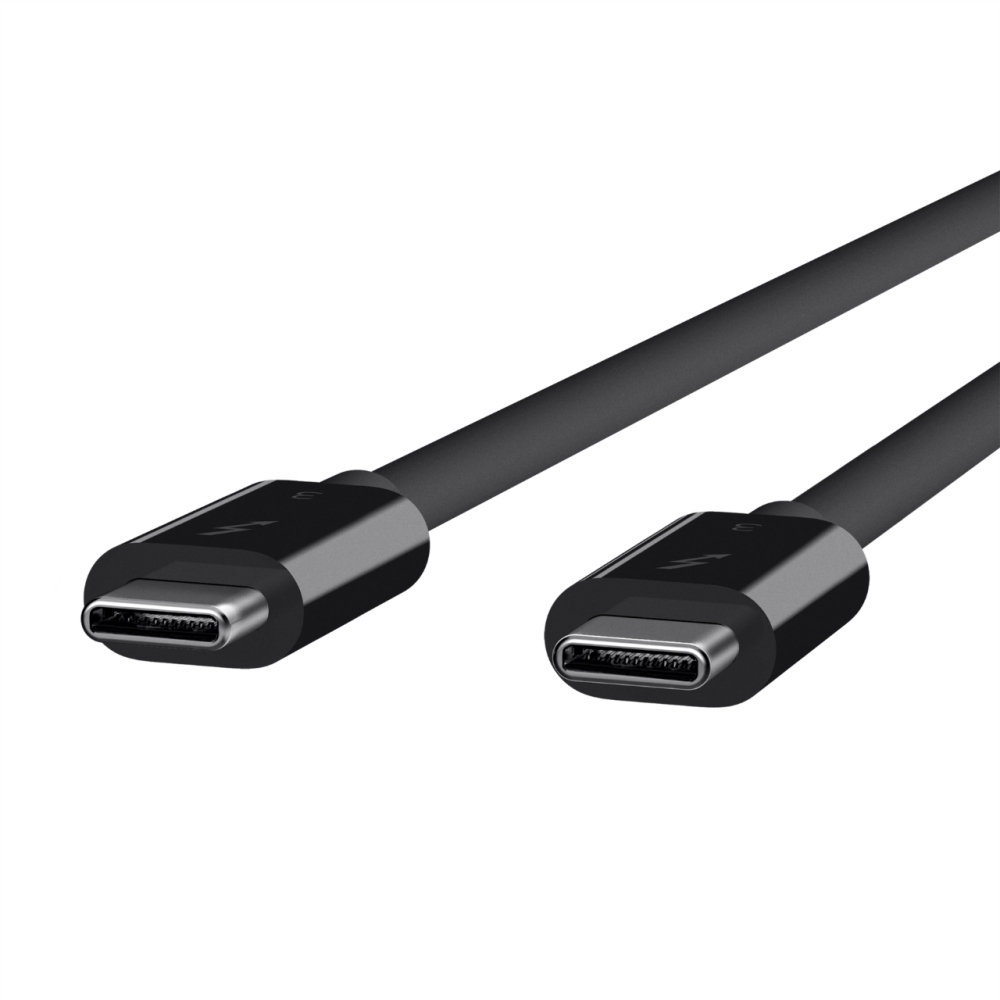
Thunderbolt is a new connection for peripherals based on PCI Express and DisplayPort architectures developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple. Your goal is to unite in a single cable High-speed data transmission, high-definition video, and up to 10 W of power. The use of optical or electrical connections is allowed, but logically only the latter allow the transmission of electricity so it is expected that most manufacturers opt for this implementation, as Apple has done. The fiber optic cables would be data connections at distances greater than 3 meters, which is the limit of copper wires.

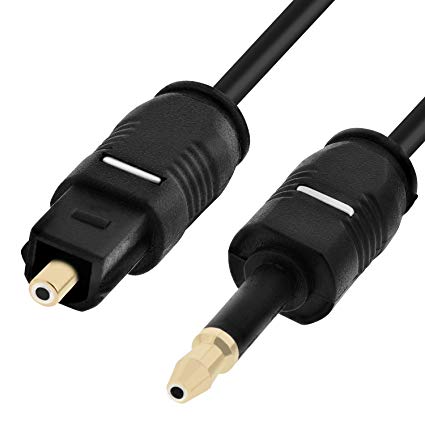
TOSLINK ( TOShiba LINK) is a connection standard for optical fiber created by Toshiba in 1983, which is based on the use of optical signals instead of electrical signals . It is generally used for the interconnection of audio equipment, although it supports different formats, both physical and data. Originally it was created for the connection between the players of CD and the signal receivers PCM . All the companies started using it and it was quickly adopted with S / PDIF how universal standard of digital optical connection. With this standard, up to 48 kHz and 20 bits are supported PCM , Dolby Digital Y DTS , but in the new multi-channel audio systems (Dolby True HD, DTS HD and DSD ) no longer has these limitations.

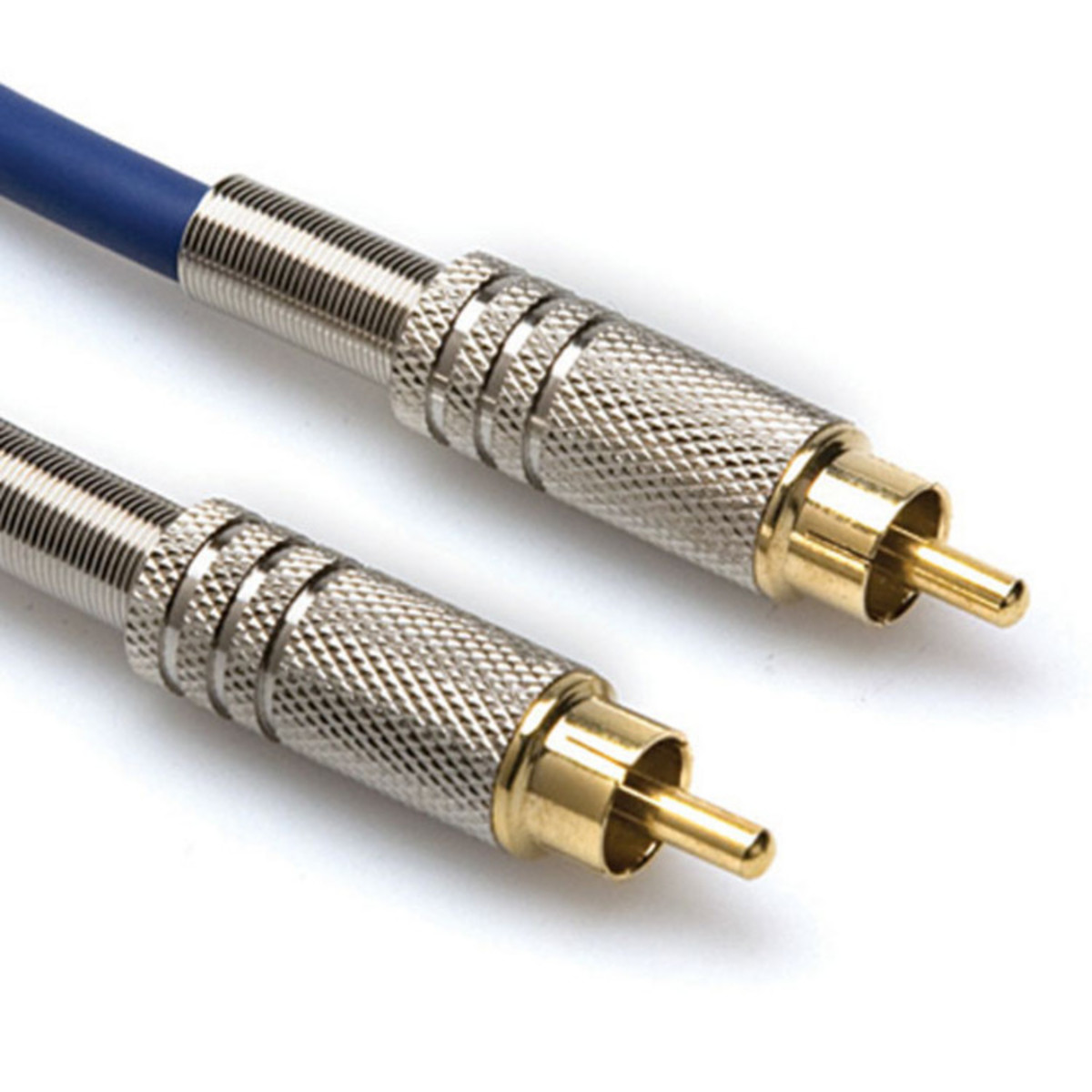
An RCA cable is a type of electrical connector that is used mostly in audiovisual equipment such as music centers, DVD players, camcorders, etc. Its name comes from Radio Corporation of America, designers of this connector in the year 1940. The male RCA connector has a positive pole at the center, surrounded by a metallic ring that acts as a negative pole, while the female connector has a hole in the center covered by a metal ring.

S / PDIF is a type of connection that we can find in a multitude of electronic devices, including desktop and laptop PCs. However, many users do not know its existence, or do not know what exactly this interface consists of. That is why we have prepared this article, with everything you need to know about S / PDIF.

13) PROCESSORS (MICROPROCESSORS) ZOCALOS, MULTICORE, HYPER READY.
The processor is the brain of the system, just processes everything that happens on the PC and executes all the actions that exist. The faster the processor a computer has , the faster the orders given to the machine will be executed. This component is part of the hardware of many devices, not just your computer
Atom-type processors .- Intel Atom processors are low energy processors and are designed to be used in netbooks and other computing devices specialized in networks, ie machines where the battery life, as well as the consumption of energy, are more important than the processing power itself.

Celeron.- These processors are designed for use in desktops or desktop PCs, focused on family use mainly for web browsing activities and basic or non-specialized computing.

Pentium.- Pentium has been used as a name for several different generations of processors. The Pentium processors of the current generation are energy efficient dual-core processors designed for desktop computers. Pentium processors have numeric indicators that, like other Intel processors, indicate higher levels of features with higher series numbers.

Core processors .- are all processors that have more than one core, which is called Core, there are two classes, which are called Core i7 and Core 2 Duo, which vary in the number of cores or processing cores. The core processors of more than one core began to be commercialized from the year 2005, popularizing since then thanks to its diverse properties that have been evolving. Currently there are Core 12 processors and up to 16 cores, but have not yet been commercialized on a large scale, being only distributed to large companies that need higher speeds and processing volumes, such as banks, financial companies, accounting firms, and specialized companies. in the handling of large-scale data such as telephone, etc.

Xeon and Itanium.- They are specialized processors in machines whose main work is the network, they are special for server use. These processors are identified by having three special indicators the letter X, (to specify that it is a high performance processor), the letter E (indicating that it is an optimized rack processor, and the letter L (indicating that it is of a CPU optimized to the use of energy.) Of these specialized processors in servers there are a core, two cores and several cores, increasing the data processing capabilities.


Intel Processors.- The processor brand that dominates the world market in this field, is Intel, which has a wide range of processors of various types, which have characteristics and specifications for certain types of equipment. Examples of this brand are the processors, Pentium, Pentium II, Pentium III, Pentium IV, Pentium D, Core, Core 2 Duo, Core 2 Quad, Celeron, Xeon, and Itanium. AMD processors.- AMD is the second company in terms of market in the field of processors, having a wide range of processors of various types with specifications for portable computing equipment, office, servers, and specialized companies. Such as the processors Athlon, Athlon XP, Athlon X2, Sempron, Athlon FX, Phenom, Phenom 2 and Opteron.

Baseboard is commonly defined as the existing area on the base plate for the placement and connection of various electronic components.

Processor sockets
This type of socket is presented as an electromagnetic support system and electrical connection, which together with a base plate is used for the connection and fixing of a microprocessor.
This is the type of socket where you can both remove and insert components in a simple and easy, where as a help has a lever that uses the same pressure to drive all the pins, while avoiding that these are damaged.
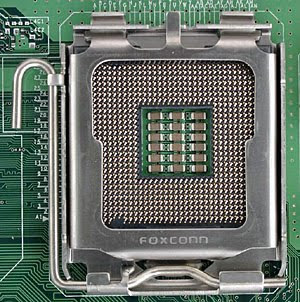
They can be employed in:
Microprocessors: is the place where the brain of the computer is inserted, where you can find several types such as: PGA, ZIF, PGA370, socket 7. Slot 1, etc.
Micro controllers
Cartridges
Integrated circuits.
Sockets of the CPU This is a piece made of plastic that is the intermediary between the microprocessor and the base plate. The pins of a processor are easily attached to a matrix of holes -GA- located in its flat upper surface.
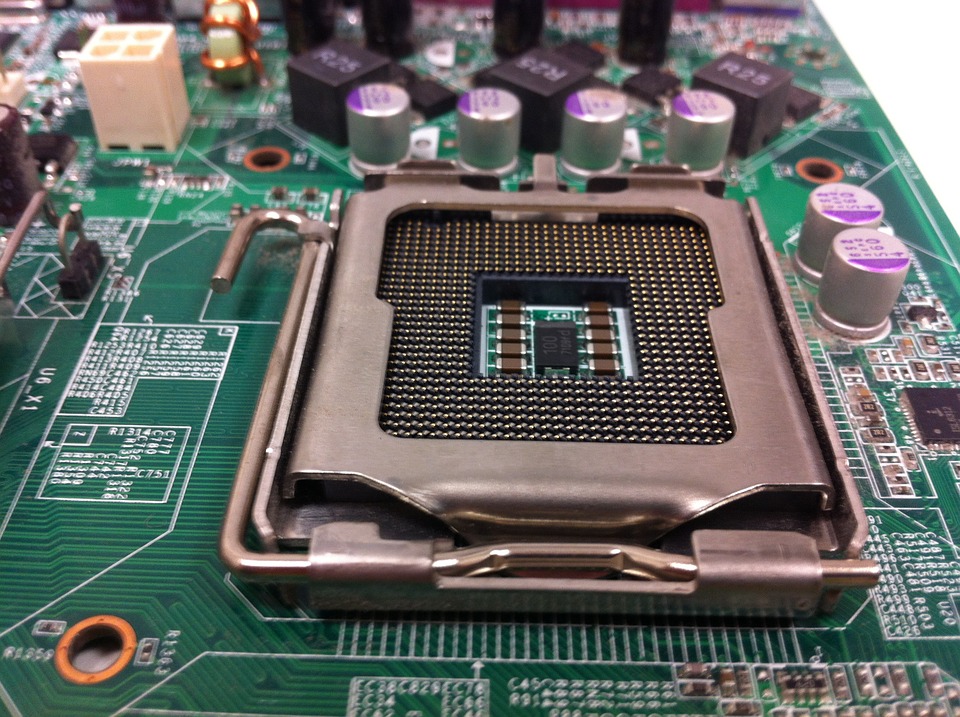
Socket for INTEL
There are several types of baseboards that were used in INTEL since its origins, such as:
Socket 423: This is the type of socket that was used in the versions that gave rise to the Pentium 4.
MPGA478 socket: this works with both Intel Pentium 4 and Intel Celeron processors.
Socket LGS775: this is the socket used in the latest version of Intel processors, which works with Intel Core Duo.
Socket 479: is the type used in those portable computers that worked or work under Intel Centrino technology.

Socket for AMD
There are several models of this type of baseboards, such as:
Socket A: is the type of socket that has been used in AMD Duron, AMF Athlon and Sempron.
Socket 754: This is the first socket to be used in the AMD Athlon 64 processor. This type allows the use of Turion and Sempron.
Socket 940: Socket that manages to be compatible with AMD dual-core and 64-bit AMD.
Socket 939: as the name implies, it is a 939 pin socket that manages to be compatible with AMD Athlon 32 and 64 bits.
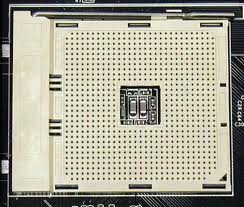
ZIF socket
This type of socket gives way to the connection of integrated circuits in printed circuits, without having to carry out welding in the equipment to be connected.
They are very used in memories and / or any component that allows the modification of informative data.

LGA sockets
In these types of sockets the needles are located in the CPU socket and there are metal contact points in the lower area of the processor.
With these you can add a larger number of needles, which offers a much more reliable source of energy to the processor.

Multicore : A multi-core processor is a integrated computer processor circuit with two or more separate processing units , called cores, that read and execute program instructions , as if the computer had multiple processors. [1] The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions (such as adding, moving data and branching) but the single processor can execute instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing the overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other computing techniques in parallel [2] Manufacturers often integrate the cores into a single integrated circuit die (known as a chip multiprocessor or CMP) or into several dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core. A multi-core processor implements multiprocessing in a single physical package. Designers can couple cores in a multi-core device either firmly or loose. For example, the cores may or may not share caches , and may implement the passing of messages or shared memory inter- core communication methods . The Common network topologies to interconnect cores include bus , ring , two-dimensional mesh Y crossbar .

hyper ready: It is a registered trademark of the Intel company to name its implementation of Simultaneous Multithreading technology also known as SMT. It allows the programs prepared to run multiple threads, process them in parallel within a single processor, increasing the use of processor execution units .
This technology consists of simulating two logical processors within a single physical processor. The result is an improvement in the performance of the processor, since simulating two processors can make better use of the calculation units keeping them occupied for a greater percentage of time. This leads to an improvement in the speed of applications that according to Intel is approximately 30%.
14) MICROPROCESSORS ARCHITECTURES OF 32 AND 64 BITS.
We can say that the architecture of a computer is everything related to the structure, organization and operation of the system.
The processors have been evolving in terms of their processing capacity, and for this the length of the data and instructions they have been able to handle and execute has had a lot to do with it.
We can then classify the processors, under this criterion, in the following types:
IA32 (Intel Architecture, 32-bit).
IA64 (Intel Architecture, 64-bit).
AMD64 (AMD 64-bit).
IA-32 (Intel Architecture, 32-bit), generically known as x86, x86-32 or i386, is the most successful architecture of the Intel processor instruction set. It is a 32-bit extension, first implemented in the Intel 80386, coming from the old Intel 8086,80186 and 80286 16-bit processors and the common denominator of all the subsequent x86 designs. This architecture defines the set of instructions for the family of microprocessors installed in the vast majority of personal computers in the world. The longevity is due in part to full backward compatibility and that the architecture has also been extended to 64-bits, without breaking the compatibility.This extension is known as Intel 64 by Intel or AMD64 by AMD (and generically referred to as x86-64 or x64) and is not related in any way to the 64-bit IA-64 architecture implemented by the Intel Itanium series.

x86-64 is an extension of the x86 instruction set used in the CPU microarchitecture. It includes additional improvements, such as duplicating the number and size of general-purpose and instruction records. It is a 64-bit architecture used by the latest Intel processors on the market. It is an architecture originally developed by AMD from the x86 architecture, and implemented under the name of AMD64. Erroneously, sometimes it is indicated with the name of x64, when its correct name is that of x86-64, since it is an extension of x86 for 64 bits. The Intel® 64 architecture provides 64-bit computing in embedded designs when combined with compatible software. Intel 64 architecture improves performance by allowing systems to address more than 4 GB of physical and virtual memory.

IA-64 (Intel Architecture, 64-bit), is a 64-bit architecture used for Intel Itanium processors . Intel’s IA-64 architecture («Intel Architecture, 64-bit»), released in 1999, is not directly compatible with the IA-32 instruction set, despite having a similar name. It has a completely different set of instructions and uses a VLIM – Very Long Instruction Word design instead of out-of-order execution (out-of-order execution). Intel Itanium, formerly known as IA-64 (Intel Architecture-64), is a 64-bit architecture developed by Intel in cooperation with Hewlett-Packard for its line of Itanium and Itanium2 processors. It uses 64-bit memory addresses and is based on the EPIC (Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing) model, explicitly processing instructions in parallel.Intel Itanium2 processors represent the most complex product design in the world with more than 1700 million transistors. This allows for solid virtualization capabilities, improved reliability and market leading performance levels. Unlike products from the few manufacturers of RISC processors that still operate, the Intel Itanium2 processor series offers freedom to the end user through a wide range of software options with more than 8,000 applications in production. High performance computing servers and systems based on the Itanium processor offer mission critical support for Windows, Linux, Unix and other operating systems.Unlike products from the few manufacturers of RISC processors that still operate, the Intel Itanium2 processor series offers freedom to the end user through a wide range of software options with more than 8,000 applications in production. High performance computing servers and systems based on the Itanium processor offer mission critical support for Windows, Linux, Unix and other operating systems.Unlike products from the few manufacturers of RISC processors that still operate, the Intel Itanium2 processor series offers freedom to the end user through a wide range of software options with more than 8,000 applications in production. High performance computing servers and systems based on the Itanium processor offer mission critical support for Windows, Linux, Unix and other operating systems.Unix and other operating systems.Unix and other operating systems.
AMD64 (AMD 64-bit), is a 64-bit architecture used for state- of-the-art AMD processors . It is an architecture originally developed by AMD from the x86 architecture, and implemented under the name of AMD64. The first processor (for personal computers) with support for this set of instructions was the Opteron, launched in April 2003. It has subsequently been implemented in multiple variants of Athlon 64 and later. The instruction set of the AMD x86-64 (later renamed AMD64) is a direct extension of the x86 architecture to a 64-bit architecture, motivated by the fact that the 4GB of memory that is directly addressable by a 32-bit CPU bits is no longer sufficient for all applications.

TYPES OF MICROPROCESSORS
adm and intel are the only two types of chips that encompass diversity in the market.
the most important features are:
Nucleus numbers : the more nucleo a microprocessor, the greater amount of information will be processed at the same time.
cache memory: it is an ultrarapid memory used by the microprocessor.
front data bus: a bus are lines (cables), traced on a plate, and is responsible for transporting different types of information.
processor speed: measured in megahertz or in gigahertz.
Power consumption: I will mention the different types of current processor
intel celeron
the portable equipment: it is apt for the basic informatic needs as to process texts.
characteristics
64 bits of the process
1mb of cache memory
800 mshz front data bus
a processor with a speed of up to 2.2 ghz
saves energy according to established standards

intel core 2 duo
portable equipment and desktop computer: this processor provides the necessary performance to perform multiple tasks at the same time.
characteristics:
memory 2 processing cores
cache memory from 2mb up to 6mb
full frontal bus. in this case, depending on the processor number, the bandwidth can be 533 mhz, 800 mhz at 1066 mhz.

intel core 2 quad
portable equipment and desktop computer: it was designed so that its performance is to process entertainment such as: high level video games, edit videos, photographs, play movies and music.
characteristics:
4 cores
cache memory of 4 mb, 6mb and 12 mb
front data bus 800 mhz and 1066 mhz
processed with speed of 2.53 ghz, 2.60ghz, 2.80ghz and 3.06 ghz

intel core i3
This microprocessor uses hyper thereading technology.
characteristics:
two core processor
3mb cache memory
ddr3 speed from 800mhsz to 1066mhz. ddr3 is the ability to make data transfer eight times faster.
processor with speed of 2.13ghz and 2.2ghz.

intel core i5
It is for everyday use, it is possible to work on two tasks at once, and have the ability to increase your speed.
characteristics:
It has 4 tracks with speed boost.
8mb cache memory
ddr3 speed of 1333 mshz
processor with speed of 2.53 ghz

intel core i7
It is appropriate to edit videos and photographs, have fun with games and of course work on several at the same time.
characteristics:
has a nucleus
cache memory of 4mb, 6mb and 8mb
ddr3 speed of 800mhz, 1066 mghz and 1333 mgz
processor with a speed of 3.06 ghz, 2.93 ghz and 2.66 ghz per core.

intel atom
Basic operations can be performed, such as writing texts and surfing the internet from anywhere.
characteristics:
has a nucleus
cache memory of 512kb
a front data bus of 667 mhz
processor speed of 1.66 mhz

15) INTEL PROCESSORS (ATOM, CELERON, PENTIUM, DUAL CORE, SERIES M, I3, I5, I7, ITANIUM, XEON) 1-6 GENERATION, AMD (ATHLON, SEMPRON, TURION, PHENOM, FUSION, BULLDOZER, SERIES A, SERIES FX)
ATOM: The Atom processors of Intel were designed with the aim of being used in portable equipment, such as netbooks, computer devices applied to the industry, mobile terminals or computers with few requirements. The Intel Atom processors are based on the Bonnell microarchitecture and have managed to stand out in the sector in a solid way by offering features that are consistent with the terminals in which they are integrated.

CELERON : This saga of microprocessors has stood out for being one of the most economical in the Intel catalog. The models that make it up are usually seen on desktops or laptops that have limited specifications and are sold at a low price. The Celeron family has been in the market since 1998 and has gained an important position in emerging markets.
PENTIUM : Pentium is a range of microprocessors of x86 architecture developed by Intel . It has single-core and multi – core versions . The first Pentium was released on March 22, 1993 as the successor to the Intel 80486 . Its code name was P54C.Origen and derivatives of the name PentiumPentium derives from the Greek «pente», which means «five», and the prefix -ium, comes from Latin.
DUAL CORE : Dual core processor, is a microprocessor in which there are two independent (physical) processors in the same encapsulation, in addition these dual core processors have for each internal processor a second level Cache memory (L2) of 1 or 2 Mb of capacity, they also share the main memory of the system for loading their own processes.
CORE I3: They have two cores and four wires, which together with their high IPC makes them an excellent solution for those who want to assemble economic equipment of high performance and efficiency. They serve to play and to work.
CORE I5: They are one of the ranges with better performance-price ratio offered by Intel and a very good choice that serves to do anything. They have four cores and four threads, and are an excellent choice for users with medium budgets. The «U» models have two cores and four wires.
CORE I7: We have four-core and eight-core processors that offer almost identical performance to the Core i5 in most cases (as long as they use the same architecture). The «U» series models have two cores and four wires. They are a good option for users who want to play everything and also use multi-threaded applications, although they do not represent an important difference compared to the Core i5 quad-core.
SERIES M: The M is by «mobile», to indicate that the processor is designed for portable systems of 4th or lower generations.
ITANIUM, XEON : Intel Xeon and Itanium processors are server CPUs designed and optimized for several server applications. These processors have three letter indicators: X specifies a high performance CPU, E is an optimized rack CPU and L indicates an optimized CPU with respect to power. There are three levels of Zeon processors. The processors of the 3000 series contain a single core, those of the 5000 series have two cores and those of the 7000 have more than two cores. The processors of the 9000 series refer to the Itanium class processors, which may have two or more cores. The higher the numbers of each series, the more features will be indicated for the processor.
1-6 GENERATION
FIRST GENERATION (1946 -1958)
Features:
In this era, computers operated with valves.
They used punched cards to enter data and program, they used magnetic cylinders to store information.
They were used exclusively in the scientific or military field.
The cartridges were extremely large.
They used a lot of energy and generated a lot of heat and they were very slow.
SECOND GENERATION (1958-1964)
Features:
They used transistors to process information.
The transistors were faster, smaller and more reliable.
They used small magnetic rings to store information and instructions.
They produced a lot of heat and were very slow.
The computer programs that were developed during the first generation were improved .
New programming languages were developed, such as COBOL and FORTRAN.
The size of computers began to decrease.
The Navy of the United States develops the first simulator.
Companies appear and computers were quite advanced for their time Like the 500 series of Burroughs and the ATLAS of the University of Manchester .
REPORT THIS AD
THIRD GENERATION (1964-1971)
Features:
Start to use integrated circuits.
The processing capacity was increased and the size of the machines was reduced.
This generation used the development of integrated circuits in which thousands of electronic components are placed in a miniature integration.
The first minicomputer was the PDP-8 of the Digital Equipmet Corporation.
FOURTH GENERATION (1971-1983)
Features:
Appearance of the microprocessor with integrated circuit in which the basic elements of the machine meet
The microprocessor was developed.
More circuits are placed inside a «chip», each «chip» can do different tasks.
The memory of magnetic rings for the memory of silicon «chips» is replaced.
The microcomputers are developed , Or Sea , personal computers, or PC.
The supercomputers are developed.
FIFTH GENERATION (1984-1999)
Features:
PC Surge As It Is As we know it today, IBM introduces its first personal computer and revolutionizes the computing sector.
In view of the accelerated march of microelectronics, the industrial society has taken on the task of also putting at that height the development of software and the systems in which they manage computers.
SIXTH GENERATION 1999 UNTIL THE DATE
Features:
The computers of this generation have combined parallel vector architecture, with hundreds of vectorial microprocessors working at the same time.
The networks of world-wide area will continue growing by means of means of communication through optical fibers and satellites, with impressive bandwidths.
ATHLON : The most advanced basic processor that AMD has ever created, for users looking for fast response and integrated Radeon ™ Vega graphics, with the innovative processor architecture they need to take advantage of the graphics card update.
Surf the Internet fast, stream videos in real time without a single cut and play the most popular high-definition sports titles at 720p.
4 threads
Advanced AMD Radeon ™ Vega graphics to enjoy 720p esports games
The innovative «Zen» processor architecture has the power you need to take advantage of the power of graphics card enhancements and play 1080p HD +
SEMPRON : Sempron has been the marketing name used by AMD for several desktop CPUs of different budgets, using different technologies and CPU socket formats. The Sempron replaced the AMD Duron processor and competes against Intel’s Celeron processor series. AMD coined the Latin name semper, which means «always», to suggest that Sempron is suitable for «daily, practical use and part of everyday life.
TURION : The AMD Turion 64 X2 was AMD’s first dual-core processor and is the direct competitor of Intel’s Core Duo. A basic feature is that it already supports 64 bits, which Intel supports only since the introduction of its Core 2 Duo. It also comes with an integrated DDR2 memory controller (2-way DDR2). However, due to the smaller level 2 cache, the performance of the first Turion 64 X2 models was a bit lower than a Core Duo at the same clock speed. The successors of the Turion 64 X2 are the Turion 64 X2 Ultra, codenamed Puma. These have the same core, but a memory controller based on the K10 architecture.
AMD PHENOM is a family of microprocessors of 64-bit of AMD , based on the K10 architecture . It includes the Phenom II X6 series of six cores , Phenom X4 and Phenom II X4 quad-core, Phenom X3 and Phenom II X3 three-core and Phenom II X2 dual-core. Other related processors based on the K10 architecture are the processors of the Athlon X2 series «Kuma», Athlon II and several models of Opteron, Sempron and Turion. The first Phenom was launched in November 2007. A second generation, improved, was launched in December 2008, called Phenom II . The processors with an «e» as suffix in the model number (eg, 245e), are low consumption models, typical values being 45 W for the Athlon and 65 W for the Phenom
AMD FX SERIES: The AMD FX series processors were the top of the company’s range until the arrival of the ZEN architecture. All of them use the AM3 + socket , they have the multiplier unlocked and they are presented in four, six and eight cores versions. This is the way to differentiate them:
First number: It is a reference to the number of nuclei. For example, the FX 8350 has eight cores, the FX 6350 has six cores and the FX 4350 has four cores.
Second number: Indicates the architecture. The FX 8350 are based on Piledriver, which is an improvement over Bulldozer, used in the previous FX 8150. The same goes for the FX 6300-6100 and FX 4300-4100.
Third number: Only indicates the working frequency of the processor. The higher the number, the higher the base frequency, without more. For example, the FX 4350 comes at 4, 2 GHz-4, 3 GHz and the FX 4300 at 3, 8 GHz-4 GHz.
BULLDOZER: based on the 32 nm process. It has had several revisions and is used in processors AMD FX, Ahtlon II X4 (and lower) and in the APUs 4000 series and higher (up to the 9000 series).
AMD Fusion: The main features of AMD Fusion tell us about discrete CPU + GPU combos , that is, dedicated. Initially they will be 2-core CPUs in 40 nanometers with DirectX 11 GPUs . They will be compatible with DDR3 memory (800 or 1,066 MHz.) And the GPU model will belong to the AMD 6000 Series for laptops. More specifically, the first models will integrate an AMDRadeon 6310.
16) RAM MEMORY DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4
DDR: Double Data Rate, means memory of double data transfer rate in Spanish. They are modules composed by synchronous memories (SDRAM), available in DIMM encapsulation, which allows the transfer of data through two different channels simultaneously in the same clock cycle. DDRs support a maximum capacity of 1 GB.
DDR2: It is the evolution of the DDR-SDRAM memory, from which it differs by operating at a higher clock speed (up to 400MHz), needing a lower voltage (only 1.8V instead of 2.5V) and having higher latencies They are mounted on 240-contact DIMM modules.
DDR3: It is the evolution of the DDR2 memory, and as in the previous case, these memories have a higher clock speed (from 400 to 1066 MHz), lower voltage (we go to 1.5 V) and higher latencies. They are mounted on DIMM modules with 240 contacts, just like DDR2 memory, however, they are not compatible because they work at different speeds and voltages.
DDR4: They are characterized by having 288 contacts (instead of the 240 of the DDR3), speeds ranging from 2GHz to about 4GHz and a consumption reduction of around 20% with respect to the DDR3. The voltage is also lower than its predecessors (between 1.2 and 1.05 for DDR4 versus 1.5 to 1.2 for DDR3). Also with DDR4 the use of double and triple channel disappears, each memory controller is connected to a single module.
The RAM memory is also a form of temporary memory, which when turned off or restart the system is again blank. This considering that at the beginning of the system the basic modules of operation (like the POST or the BIOS), often registered in ROM, make a check of the RAM memory to make sure that it is operative and can be downloaded in it the necessary software for start the system.
17) SATA, PATA OR IDE CONNECTORS
IDE: In general, the IDE / ATA connector of the motherboard is a simple 40-pin connector to which a flat cable is fastened, which goes from the base plate to the disk drive. These pins are a subset of the 98 contacts of the 16-bit ISA slots. The reason is that a disk controller never needs more than 40 ISA bus signals.
SATA: The sato connector is very thin and lightweight, and barring some new introductions in the present, it does not have an insurance that affirms it on the motherboard or on the device, which makes it a very weak connector, too exposed to unplugging or make bad contact with a simple transfer of a PC (in fact the first thing I do when a PC does not boot is to check the SATA cable, and believe me, it is a very high percentage) this is something unforgivable for so many companies and engineers involved.
PATA: PATA is an abbreviation of adjunct of advanced technology in parallel. It is a regular interface that is used within PCs to connect all kinds of storage devices such as hard drives, CD drives or DVD and the solid state disks to the motherboard. The interface connector PATA consists of thirty four pins and connects to A wire Plano tape nearly two inches wide. It does not support hot swapping. Cables PATA supports sixteen bits of data transfer at a time. Although PATA standards recommend cables up to 18 inches in length, twice the length of the cables are known to work smoothly in performance. Longer cables may be necessary sometimes in the case of the Towers degran size with external hard drives or to improve cooling inside.
18) EXPANSION SLOTS AGP, PCI, PCI EXPRESS
Ports or PCI BUS : PCI BUS. It means Interconnected Peripheral Component and it is a 32-bit communication bus that performs its functions at 33Mhz, transferring data to and from RAM. at 133Mbits / s, a satisfactory speed even for PCI-type 2D graphics cards. Thanks to the PCI bus, the processor can work in other more complex functions while it develops manipulations of texture and calculation of polygons for example. The PCI slots vary depending on the bits to be transported; This is the case of 32-bit PCI slots and 64-bit PCI slots, which are the most recent. For the electrical requirement there are also three types of PCI cards: 5-volt PCI for desktop computers, 3.3-volt PCI for laptops and Universal that can be used for the two previous systems.
Ports or AGP BUS : AGP BUS. It means Advanced Graphics Port and is a system used for the connection of peripherals on the motherboard that transfers data from the microprocessor to the peripheral that is connected to the bus. The AGP BUS offers several types of operation:
AGP 1X with speed of 66Mhz transfer of 264MB / s and voltage of 3.3V.
2X AGP with 133Mhz transfer speed of 528MB / s and 3.3V voltage.
AGP 4X with speed of 266Mhz transfer of 1GB / s and voltage of 3.3 or 1.5V.
AGP 8X with speed of 533Mhz transfer of 2GB / s and voltage of 0.7 or 1.5V.
Normally the motherboards only bring an AGP BUS slot.
PCI Express ports: PCI Express BUS. The latest technology, came to replace the PCI and AGP buses, has great transfer speed. It has two speeds, the PCI Express 1X with a speed of 133 MHz for devices such as audio and TV cards. And the PCI Express 16X with speed of 2128Mhz for graphics cards .
19) VIDEO CARD DEDICATED AND INTEGRATED IN THE BOARD (CROSSFIRE BRIDGE, SLI BRIDGES).
The graphics card, or GPU, is one of the essential parts of a computer since it is responsible for processing everything we see on our computer screen, from the desk to the games. Independent of the brand and its model, there are two large groups of graphics that we must know and differentiate in order to know how far our computer can reach: the integrated graphic cards and the dedicated graphics cards . The first thing we must do is to know how to differentiate between both types. The Integrated graphics cards are those whose chip is integrated in the motherboard itself or in the CPU. These graphics usually offer a fairly limited performance, but, in return, are usually quite cheaper, being almost always present in inexpensive laptops. The Dedicated graphics cards, on the other hand, are a second GPU installed independently on the motherboard.
CROSSFIRE BRIDGE: is the name given to the Multi GPU system of ATI / AMD that was designed as a counterpart to the SLI of nVidia . This system allows, using a certified Crossfire board, to connect up to four graphic cards that support this technology in PCIe x16 slots . The total bandwidth that each card receives will depend on the configuration of PCIe transmission lines that have the north bridge included in the motherboard .
SLI BRIDGES : Premium quality brushed aluminum finish with lighting system and ROG logo. Available in two, three and four way SLI configuration for wide compatibility with ASUS and NVIDIA video cards.
20) TRANSMISSION MEDIA (WI-FI (A, B, C), BLUETOOTH, IRDA, RJ11, RJ45, RS-232)
WIF A, B, C: Wireless Fidelity) is the popular name for RLAN systems that use the IEEE 802.11 family of standards .
Officially, it is the name of the certificate that the Wi-Fi Alliance grants to IEEE 802.11 products that pass their interoperability test. The interoperability of products from different vendors is tested to ensure that products from these vendors can work together in a wireless LAN ( RLANs) ). If a product passes the test, it is allowed to carry the Wi-Fi logo.
The original Wi-Fi certification program covered only the IEEE 802.11b products. The certification program extends to include products based on other members of the IEEE 802.11 family as well.
BLUETOOTH: is an industrial specification for wireless personal area networks (WPAN) created by Bluetooth Special Interest Group, Inc. which allows transmission of voice and data between different devices over a radio frequency link in the ISM 2.4 GHz band.
IRDA: Association of infrared data (IrDA), «Association of infrared data», defines a physical standard in the form of infrared transmission and data reception. IrDA was created in 1993, among: HP, IBM, Sharp and others. This technology is based on light rays that move in the infrared spectrum.
RJ11: RJ11 connector. The RJ11 connector (RJ stands for Registered Jack) is the most used connector for telephone lines. It is similar to an RJ45 connector but smaller. In a computer, it is usually used to connect the modem.
RJ45: is a physical interface commonly used to connect computer networks with structured cabling (categories 4, 5, 5e, 6 and 6a). It has eight pins or electrical connections, which are normally used as twisted pair cable (UTP) ends. It is part of the Federal Code of Regulations of the United States.
RS-232: (Recommended Standard 232, in Spanish: «Recommended Standard 232»), also known as EIA / TIA RS-232C, is an interface that designates a standard for the exchange of binary data in series between a DTE (Terminal Equipment data, «Terminal data equipment»)
21) REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS (DISSIPATOR, FAN, LIQUID).
A DISSIPATOR is an instrument that is used to lower the temperature of some electronic components. Its operation is based on the second law of thermodynamics , transferring the heat from the hot part that is desired to dissipate into the air . This process is promoted by increasing the contact surface with the air allowing a faster removal of excess heat.
FAN: Vehicles equipped with an air conditioning system need a cooling fan of higher capacity. Thanks to the advanced fluid dynamics calculation methods used, the DENSO cooling fans guarantee a lower noise level and higher performance. Although it is usually mounted behind the radiator, in some applications the cooling fan is mounted in front of the radiator to increase the air flow at low travel speeds or when the vehicle is stopped.
The cooling fan operates with a solenoid valve controlled by temperature and coolant pressure sensors, activating only when necessary.
DENSO cooling fans meet the most extreme needs of vehicles.
LIQUID: The liquid cooling or Watercooling is a cooling technique that uses water instead of heat sinks and fans (inside the chassis ), and thus achieves excellent results in terms of temperatures with huge overclock possibilities . It is usually done with watertight water circuits.
Water, and any coolant, have a higher thermal capacity than air. From this principle, the idea is to extract the heat generated by the components of the computer using water as a medium, cooling it once out of the cabinet and then reintroducing it.
22) HARD DISCS CONNECTIONS (SATA, IDE) TECHNOLOGIES (HDD, SCSI, SSD, SSHD).
SATA: (Serial ATA) is the one currently used by the next generation desktop and laptop computers, it is a novel interface that uses a serial bus for data transfer, of course faster and more efficient than the IDE system. For SATA there are three versions of speed SATA 1 has a transfer rate of up to 150MB / s, SATA 2 with transfer of up to 300MB / s which is the most sold in the market and finally the SATA 3 with a transfer rate of up to 600MB / s that is just beginning to come to market, the SATA version of hard drives is much more compact than the IDE and allows hot-plugging.
IDE is a unit that uses a parallel ATA connection, called IDE informally. The term IDE is synonymous with Integrated Drive Electronics Interface (Integrated Electronic Unit Interface). The first time hard disks used the IDE interface was in 1986.
TECHNOLOGIES (HDD, SCSI, SSD, SSHD).
HDD : are the conventional hard drives, its acronym comes from the English «Hard Disk Drive», this technology is the oldest of the three since it is the only one that requires mechanical movement to function. The hard disk works in the following way, inside it has a magnetic head that goes encoding tiny sectors of a metallic disk in rotation at high speeds, these heads write on the disk using binary code (0 and 1).
SSD : or disk in solid state are the natural evolution of the HDD technology or hard disk, solid state disks do not require mechanical movement, so they do not heat up as much, make less noise and require less energy. SSDs use the same SATA connector that the HDD, despite this achieve much higher speeds reaching 6Gbps (540MB / s) of read and write.
SSHD: This new technology introduced by Seagate comes to take advantage of both technologies, the speed and reliability of the SSD and the capacity and price of the HDD, this way we get fast disks with a lot of capacity for a slightly higher price than the HDD. of a conventional hard disk. The SSHD are sometimes more useful than the SSD, discs that given their price are often wasted storing gigas and gigas of small files.
SCSI : is the acronym for Small Computers System Interface and is a standard that is used to define the connection of devices to the motherboards of PCs. Do not be fooled by the word Small since this standard is intended above all to be used on large servers. In Spanish it is usually pronounced as «escasi». The world of hard drives is quite complex and does not stop at the needs of the home user. The storage standard par excellence of the first PCs was the IDE . Its main advantage is that you could connect up to two devices using a single cable, thus reducing circuitry on the motherboard and therefore price. Once the cost of that low circuitry ceases to make sense that shared cable. Then appears the SATA that allowed a single disk by cable and therefore higher speed. Its disadvantage is that we need a connector for each disk.
23) MULTI CARD READER PC (SM, SD, MS (MEMORY STICK), MEMORY STICK PRO (MS-PRO), MS-DUO, MICROSD, MINISD, MULTI MEDIA CARD (MMC), ESATA)
A memory card reader is a device for accessing data on a memory card such as CompactFlash (CF), Secure Digital (SD) or MultiMediaCard (MMC). Most card readers also offer writing capability, and along with the card, this can work like a pen drive. Some printers and smartphones have a built-in card reader, as do most personal computers and most tablets.
A multiple card reader is used for communication with more than one type of flash memory card. Several card readers have no built-in memory capacity, but can accept multiple types and styles of memory cards.
The number of compatible memory cards varies from one reader to another and can include more than 20 different types. The number of different memory cards that a multiple card reader can accept is expressed as x-in-1, where x is a number that indicates the number of memory cards accepted, such as 35 in 1. There are three categories of memory card readers. cards ordered by type and number of card slots: individual card reader (for example, 1x only for SD), multiple card reader (for example, 9 in 1) and serial card reader (for example, 4x only for SD)
Some types of memory cards with their own USB functions do not need the card reader, such as the Intelligent Stick memory card, which can be connected directly to a USB slot.
The USB device class used is 0x08.
Modern UDMA-7 CompactFlash and UHS-I Secure Digital cards offer data rates greater than 89 MB / s and up to 145 MB / s, [1] when used with memory card readers with USB 3.0 data transfer capability.
24) READING AND BURNER UNITS (CD, DVD, BLUERAY).
The CD-ROM drive allows you to use optical disks with a higher capacity than 3.5-inch floppies: up to 700 MB. This is its main advantage, since CD-ROMs have become the standard for distributing operating systems, applications, etc. The use of these units is very widespread, since they also allow to read compact audio discs.
DVD: DVD-ROM drives are apparently the same as CD-ROM drives, they can read both DVD-ROM and CD-ROM discs. They differ from the CD-ROM reading units in that the support used has up to 17 GB capacity, and in the speed of reading the data. The speed is expressed with another number of the «x»: 12x, 16x … But now the x refers to 1.32 MB / s. Thus: 16x = 21.12 MB / s.
BLUERAY: It is a device that mounts in the bays of 5.25 «of the cabinet, basically integrates within itself a special blue laser beam emitter to read the recorded data in a CD (» Compact Disc «), in a DVD (» Disc Digital Versatile «) and the DB (» Blu-ray Disc «), a motor to turn the disc and a tray to place them.After reading the data, this unit is also responsible for sending them through a cable to the card main (Motherboard) to be processed.
25) JOYSTICK, CONTROL CONTROLS, DIADEMS, MICROPHONE.
JOYSTICK: It is a device of control of two or three axes that is used from a computer or videoconsola until a space shuttle or the airplanes of combat, passing by cranes.
CONTROL CONTROLS: It is an electronic device used to perform a remote operation (or remote control) on a machine. The term is generally used to refer to the remote control (usually called simply «the command» or, in Latin America, «the control «) for the television or other type of home electronic device, such as DVD, Hi-Fi, computers, and to turn a switch on, turn off the alarm, or open the parking door.
DIADEMAS: There are the so-called headband microphones that are those, which, as the name implies, adhere to the head like any headband, which allows the user greater comfort no longer need to hold it with their hands, which allows them to perform other activities.
MICROPHONE: The microphones are the transducers responsible for transforming acoustic energy into electrical energy, allowing, therefore, the recording, storage, transmission and electronic processing of audio signals. They are dual loudspeaker devices, both transducers constituting the most significant elements in terms of the sound characteristics that superimpose the audio signals.
26) KEYBOARD AND MOUSE WIRELESS AND WIRELESS (USB, PS / 2, BLUETOOTH, WIFI).
WIRED KEYBOARD: It is an input peripheral or device, partly inspired by the keyboard of typewriters, which uses a set of buttons or keys, to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches that send information to the computer.
WIRELESS KEYBOARD: Usually common keyboards where the communication between the computer and the peripheral is done through infrared rays, radio waves or by bluetooth.
MOUSE WIRELESS: It is a pointing device used to facilitate the management of a graphic environment on a computer. It is usually made of plastic and is used with one of the hands. detects its relative movement in two dimensions by the flat surface on which it rests, usually reflected through a pointer or arrow on the monitor.
WIRELESS MOUSE: In this case the device lacks a cable of a cable that communicates with the computer, instead it uses some kind of technology Wireless For this, it requires a receiver that receives the wireless signal that produces, through batteries, the mouse. The receiver normally connects to the computer through from a USB or PS / 2 port
USB PORTS: It is a general way of naming an interface through which different types of data can be sent and received. This interface can be physical, or it can be at the Software level (for example, the ports that allow the transmission of data between different computers).
PS / 2 PORT: It is a port developed by IBM to connect the mouse or the keyboard to the computer. The Most PCs have a PS / 2 port so that the serial port can be used to connect another peripheral.
BLUETOOTH: It’s an industrial specification for Wireless Networks of Area Personal (WPANs) that allows the transmission of voice and data between different devices through a radio frequency link in the ISM band of 2.4 GHz
Infrared: The infrared requires a communication line between transmitter and receiver, which is essential to the 1 ANDO view for effective transmission. L as frequencies of the infrared band do not allow the penetration to 1 Andol walls, one ándole an advantage importance RF operating Bluetooth. The infrared communication will always be one by one, leaving aside the multipoint point configurations. WIFI : It’s a brand of the Wi-Fi Alliance, the
organization commercial adopter, testing and certify that the equipment meets the standards 802.11 related to networking Inalambricas of areas local.
27) STABILIZERS, UPS, IEC CONNECTOR.
Stabilizers, UPS, IEC connector : A voltage stabilizer is an electronic or electromechanical equipment, designed to provide a stabilized voltage at its output (230 volts or 380 volts), although at its input the voltage is higher or lower than the utilization value .
UPS: it is a power source that has a battery to continue supplying power to a device in the event of an electrical interruption. The UPS is called in Spanish UPS (uninterruptible power supply). UPS stands for uninterrupted power supply in English.
IEC connector: (International Electrotechnical Commission) is the common name of the set of thirteen electrical power connectors and thirteen plug-in panels, defined in the IEC 60320 specification (formerly IEC 320) of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
28) IMPACT IMPRESSORS (MATRICIALES, NOT MATRICIALES), WITHOUT IMPACT (THERMAL, INJECTION OR INK CHEER, LASER).
The dot matrix printer : or dot matrix printer is a type of printer with the print head that moves from left to right printing on the page by impact , pressing an ink ribbon against the paper, similar to the operation of a machine to write . Unlike the typewriters or margarita printers , the letters are obtained by selecting points from a matrix, and therefore it is possible to produce different types of letters, and graphics in general.
Because of the mechanical pressure that printing requires, these printers can create carbon copies . This technology was first commercialized by Digital Equipment Corporation . [ Citation needed ] Technically, the term «matrix» is inappropriate, because almost all inkjet printers ink , thermal printers and Laser printers produce dot matrices. However, this word seems to have been reserved for impact matrix printers.
Non-matrix impact printer: prints without impact. This is the name given to printing made by a set of devices, usually connected directly to the computer, that generate the image without the printer touching the support.
thermal printer: It is a high-speed electromechanical device, which has the function of receiving digital information from the computer; for by means of heat, a beam of light and an ink ribbon, to capture it on the sheet, (there is also a variant in which the beam of light records directly on special paper without the need for ribbons). It prints basically in black color although at the moment they are in the market some that have the capacity to print in 2 or 3 colors, it is used for the printing of purchase vouchers.
Inkjet Printers: A printer inkjet printer uses one of the most popular printing technologies today. The relatively low costs and multi-purpose printing skills make inkjet printers a good choice for small businesses and home offices.
Inkjet printers use a fast-drying, water-based ink and a printhead with a series of small nozzles that spray ink to the surface of the paper. The print assembly is driven by a motor fed by a belt that moves the head along the paper.
The inkjet printers were originally manufactured to print only in monochrome (black and white). However, since then the head has expanded and the nozzles have been increased to include cyan, magenta, yellow and black. This combination of colors (called CMYK) allows the printing of images with almost the same quality of a photographic development laboratory (when certain types of paper are used). When combined with clear print quality and high reading quality, inkjet printers become the all-in-one selection for monochrome and color printing needs .
Laser: It is an electromechanical device, which has the function of receiving digital information from the computer, by means of powdered ink and a laser beam, to capture the information in a physical medium. They usually use a black toner, although laser printers have also been designed to print in color. The devices that can currently also directly receive data are portable hard drives , USB sticks , a local network (LAN) RJ45 connector or from a scanner .
29) TONER, CARTRIDGES, CONTINUOUS INK SYSTEMS.
Toner : When we speak of toner, we refer to the powder that, electrically charged, consists of two types of elements, on the one hand the pigments and on the other, the plastic. In the first case it is the elements that give color to the text that we are going to print. The function of the plastic is precisely to mix with those pigments, subsequently melting through the fusion unit of the toner Meaning of the word toner: this word has several meanings, but we only use it as a mixture of dust to form images using laser xerography technology.
Cartridges : An ink cartridge or Inkjet cartridge is a replaceable set of a printer that contains the ink and, often, also the printhead itself that projects the ink onto the paper during printing. The name derives from the fact that it corresponds to a hard container that It is inserted inside the machine and contains ink either on the basis of water or a special solvent. Each ink cartridge contains one or more independent ink tanks. Some manufacturers also add electronic contacts and a chip that communicates with the printer. The replacement of consumables is an important use of the cartridges. These are used in printers to contain ink or toner.
Systems Continuous Ink : A continuous ink system, English Continuous Ink Supply System (CISS), also known by the names inkjet bulk , or simply Bulk kit (in English , «in batch.») A continuous ink system has many advantages that have made it popular in many countries around the world: The cost of ink is reduced, compared to the continuous cartridge replacement, it has little maintenance (only in the If the cartridge is damaged, a deep maintenance must be done). Another important advantage is that you can continue to recharge the tanks as many times as necessary, if the head is not damaged .
30) SBC REDUCED PLATE COMPUTERS (ARDUINO, RASPBERRY PI, ORANGE PI, BANANA PI)
Arduino: the designs of the Arduino boards use several microcontrollers and microprocessors. In general, the hardware consists of an Atmel AVR microcontroller, connected under the «minimum system» configuration on a printed circuit board to which you can connect expansion boards (shields) through the arrangement of the input ports and exit. Present on the selected plate.
Raspberry Pi: is a low-cost computer, a single-board computer or a low-cost single-card computer (SBC) developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation, with the aim of stimulating computer education in the schools.
Orange Pi: is a single-board open source computer, based on Raspberry Pi1 but lower priced and manufactured by Shenzhen Xunlong Software CO., Limited. It can work with Android 4.2, Android 4.4, Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, Raspbian, ArchLinux, openSUSE, OpenWrt and other operating systems. It uses the AllWinner A20 SoC processor and has a memory that goes from the 256MB of Orange Pi Zero to the DDR3 SDRAM of 2GB of the larger cards. It has a standard TF card slot .
Banana Pi: Banana Pi is a small plate similar to the Raspberry Pi but with a more powerful processor and 1 GB of RAM. It is based on an Allwinner A20 capable of running Android, Lubuntu or Raspbian, for example. It is a small plate of characteristics for those who want to take full advantage of its power.
